Table of Contents
FOOD SAFETY GUIDES

Is Paraffin Wax In Food Toxic?
Paraffin wax possesses moisture and oxygen-barrier properties. Moisture and oxygen are external factors that negatively affect the shelf life and quality of food. Certain types of cheeses, for example, require ample amount of moisture to retain its flavor, appearance, and texture for an extended period of time. Gouda, Cheddar, and Queso de Bola (Philippine cheese) often come enclosed in red paraffin wax.

Silica Gel In Food Packaging: A Harmless Ingredient Explained
Silica gel is an example of a desiccant. Desiccants are substances that have the capability to absorb and retain moisture. In many industries, silica gel is often used. It is made of silicon dioxide (SiO2), the same compound found in quartz and sand. Its porous structure allows it to absorb water molecules from the surrounding environment.

How Long Does Powdered Milk Really Last?
Powdered milk, alternatively referred to as dry milk or milk powder, is a dairy product obtained from liquid milk using a dehydration method. The liquid milk undergoes evaporation to eliminate a substantial portion of its water content. Subsequently, the concentrated
FOOD ADDITIVES

Why Calcium Propionate Is In My Bread?
During the earliest days of making bread, the ingredients that bakers would use are relatively simple—flour, salt and yeast. The practice of using yeast to make bread rise started as early as 1300 BC. During this period, bread is eaten

Why Sodium Citrate Makes Good Cheese
Cheese comes in an incredible variety of textures, flavors, and aromas, offering something for everyone. From soft and spreadable to hard and crumbly, mild and creamy to sharp and tangy, the possibilities are endless. This vast variety allows it to
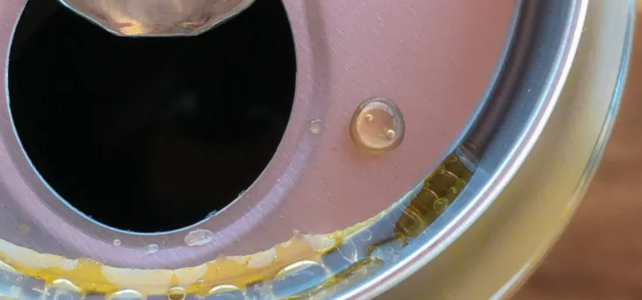
What Phosphoric Acid Does In Soda
Ever cracked open a can of your favorite fizzy drink and decided to give the ingredients list a quick scan? If you have, chances are you’ve come across the mysterious-sounding “phosphoric acid.” What on earth is it, and what’s it
FEATURED

Why Sodium Citrate Makes Good Cheese
Cheese comes in an incredible variety of textures, flavors, and aromas, offering something for everyone. From soft and spreadable to hard and crumbly, mild and creamy to sharp and tangy, the possibilities are endless. This vast variety allows it to

Why One-Day-Old Rice Should Be Used For Fried Rice
When the cooked rice is refrigerated, the starch molecules gradually undergo a reformation process called retrogradation. In food chemistry, retrogradation refers to the phenomenon in which starch returns or reverts to a crystalline structure as it cools down. The result of retrogradation is the formation of resistant starch. This is the same reason why bread in the refrigerator hardens over time.

The Benefits Of Using Himalayan Salt In Cooking
Derived from the Khewra Salt Mine in the Himalayan foothills of Pakistan, Himalayan salt primarily comprises sodium chloride, supplemented by trace minerals like magnesium, potassium, and calcium that contribute to its pink hue. This salt deposit’s origins trace back millions

Food Science: Why Is Cheese Yellow?
If cheese is primarily made from milk, which is white in color, why is cheese yellow, then? Well, most cheese, in general, is yellow because of natural pigments called carotenoids. The main providers of milk for cheese production are cows, and their diet typically consists of grass, hay, or silage. These feed sources contain carotenoids, specifically beta-carotene, which acts as a precursor to vitamin A and contributes to an orange-yellow hue in cheese.